Несколько полезностей для начинающих любителей dsd
Содержание:
- Why sample rate above 44.1 kHz is need
- How DSD works?
- DSD vs FLAC, WAV, PCM comparison
- Ресемплинг DSD
- Структура цифрового звукового тракта
- Frequently Asked Questions
- How to play DSD?
- DSD editing software
- Какие бывают файлы DSD?
- DSD history
- What is Hi-Res audio? How it works? Why does High-Resolution is need?
- DSD music downloads
- PCM vs DSD vs DXD vs Analog sound quality
Why sample rate above 44.1 kHz is need
Sample rate 44100 Hz:
- cover audible band 0 … 20 000 Hz and
- have 2050 Hz reserve for the transient band of low-frequency filter (in ADC and DAC).
However, the reserve is considered abstractly. Real-life filters are analog. And have wide transient band.
To solve the a wide transient band issue, digital filters and higher sample rates or oversampling are used.
But digital filters are not ideal and have:
- ringing audio (property of digital filters);
- limitation of the minimal size of the transient band (due to limited computing resources of example).
To reduce necessity in «hard» efforts to proper filter transient band, higher sample rates (including DSD) may be applied.
Read details issues of sample rate and filters:
How DSD works?
Free DSD downloads >
Free Hi-Res downloads >
Free DSD converters >
Free DSD players >
DSD64 vs 128 vs 256 >
As rule, DSD has explained in the time domain: positive samples increase level, but negative decrease and analog filter smooth «saw» form of signal.

Into DSD analog-to-digital converter (ADC), measuring «saw» signal is compared with input analog signal.
DSD and PCM difference

At the ADC output «1» is present. And measuring-signal level grows until it exceed current level of the input analog signal.
It cause switching output signal to «0». And measuring signal begin to reduce level.
When the measuring signal level is lesser input signal of the ADC, its output is switched to «1». And measuring signal grows until the exceeding of input signal.
Read how to sigma-delta modulator works…
Such explanation causes difficulties in understanding what is actual difference between PCM and DSD and how to process DSD. Probably, it create myth about «native» DSD processing. About the processing read below in «DSD editing software» part.
Instead the explanation, in the author opinion, the easiest way to understand how to DSD works and process it is its spectrum considering.
To estimate DSD and PCM sound quality, the quantization-noise level is main criteria.
There is an explanation, that DSD has super high sample rate and, thus, super low bit depth 1-bit does not matter for noise.
But DSD 64 sampling rate (2,8 MHz = 44.1 kHz * 64), it is not enough to be better CD audio (see ).
To decrease noise level, noise shaping is used.
1-bit quantization-error (noise) energy have a significant level.
However, there is, so-called noise shaping of the spectrum is used. And quantization-error energy is re-distributed.
Noise shaping (NS) of 1-bit signal (spectrum)

The quantization-noise spectrum (at the left of the picture) has level comparable with a musical signal. Sigma-delta modulator pushes significant part of the energy from low to high-frequency range, out of audible band (0 … 20 kHz).
Noise shaping is implemented in sigma-delta modulator (a.k.a. DSD modulator).
When the 1-bit record is played back, low-frequency filter into sigma-delta demodulator (a.k.a. DSD demodulator, DSD decoder) cut the noise.
DSD decoder (demodulator)

Therefore, at spectrum error level into the audible range is comparable with multibit pulse code modulation’s (PCM) one.
Also, sigma-delta modulation may have multibit resolution. Read details below and watch the video at this page.
DSD vs FLAC, WAV, PCM comparison
Free DSD downloads >
Free Hi-Res downloads >
Free DSD converters >
Free DSD players >
DSD64 vs 128 vs 256 >
Watch and share: DSD versus FLAC comparison
What is DSD? Quick explanation

Bit depth define audible noise. More bit depth is lesser noise.
At the picture, we can see that bit depth decreasing achieved through using only part of the full signal frequency band. Other words, if we want to reduce bit depth, we must increase the sample rate to keep the audible noise level.
Read details of the format comparison in the table: DSD vs WAV vs PCM vs FLAC vs DXD
| Feature | DSD | FLAC | WAV | PCM | DXD |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Coding | sigma-delta modulation | pulse code modulation | pulse code modulation | pulse code modulation | pulse code modulation |
| Sample rate | 44100 x 64 x N | up to 384’000 Hz | up to 2’147’483’648 Hz | no limit | 352 / 705 kHz |
| Bit depth |
1 bit, |
16 … 24 bit, |
16 … 64 bit integer, |
multibit | 24/32 bit |
| Band for audio signal | Low part of the band | Full band | Full band | Full band | Low part of the band |
| Medium | file, optical disk: SACD | file | file | file, digital tape, optical disk: CD, DVD |
Note: WAV and FLAC are PCM implementations.
Read which is better DSD or FLAC (Infographic) >
Read more about audio file formats >
Direct Stream Digital (sigma-delta modulation) is like to pulse code modulation, but quantization error spectrum is shaped for decreasing noise into the audible range.
We can apply for usual PCM. But the difference here is band reserve for pushed noise out of audible frequency range.
DSD versus PCM

PCM have lesser band reserve (above audible range) than sigma-delta modulation format, but pulse code modulation has higher bit depth.
Noise shaping for pulse-code modulation is implementation matter too, like sigma-delta modulation.
Therefore, no format advantages as itself. But implementation makes a difference.
Sigma-delta-modulation decoder (demodulator) is 2-position (1 / -1) voltage generator and low frequency filter. It is simpler than pulse-code-modulation hardware demodulator. Because pulse-code demodulator contains multi-voltage matrix or 1-bit decoder(s). So we have more abilities to make cheaper 1-bit DAC better than multibit one.
Read details here >
Also, look to infographic DSD versus FLAC >
Ресемплинг DSD
Релемплинг DSD (или передискретизация) это цифровая обрабока сигналов. Выполнается с помощью кратного апсемплинга/даунсемплинга с цифровой фильрацией.
Перед конвертацией, DSD файл преобразуется без потерь в мультибитовый аудиопоток, подходящий для обработки. Этот поток обрабатываетсяи конвертируется обратно в DSD с помощью модулятора.
Ресемплинг 1-битового аудио ведет к небольшим потерям, сравнимым с потерями при ресемплинге PCM. Эти потери определяются качеством реализации обработок сигнала.
Однако, звуковоспроизводящая аппаратура может иметь различный уровень искажений на различных частотах дискретизации. Поэтому, ресемплинг можеть дать преимущество, если DSD конвертирован на частоту дискретизации, которая воспроизводится данным ЦАП (DAC) с минимальными искажениями.
Ресемплинг DSD аудио файла для частоты дискретизации,
на которой используемый DAC имеет минимальные искажения

Структура цифрового звукового тракта
При проигрывании музыки происходит примерно следующее: плеер при помощи кодека, выполненного в виде устройства или программы, распаковывает файл в заданном формате (FLAC, MP3 и другие) или считывает данные с CD, DVD-Audio или SACD-диска, получая стандартный поток данных PCM. Затем этот поток передается через USB, LAN, S/PDIF, PCI и так далее в I2S-конвертер. В свою очередь, конвертер преобразует полученные данные в так называемые кадры интерфейса передачи данных I2S (не путать с I2С!).
I2S
I2S — это последовательная шина передачи цифрового аудиопотока. Сейчас I2S — стандарт для подключения источника сигнала (компьютер, проигрыватель) к цифроаналоговому преобразователю. Именно через нее подключается напрямую или опосредованно подавляющее большинство ЦАП. Существуют и другие стандарты передачи цифрового аудиопотока, но они используются гораздо реже.
Выход (вход) I2S на печатных платах
Шина I2S может состоять из трех, четырех и даже пяти контактов:
- continuous serial clock (SCK) — тактовый сигнал битовой синхронизации (может называться BCK или BCLK);
- word select (WS) — тактовый сигнал кадровой синхронизации (может называться LRCK или FSYNC);
- serial data (SD) — сигнал передаваемых данных (может называться DATA, SDOUT или SDATA). Как правило, данные передаются от передатчика к приемнику, но бывают устройства, которые могут выступать и приемником, и передатчиком одновременно. В таком случае может присутствовать еще один контакт;
- serial data in (SDIN) — по этому контакту данные движутся в направлении приема, а не передачи.
SD или SDOUT служит для подключения цифроаналогового преобразователя, а SDIN используется для подключения аналого-цифрового преобразователя к шине I2S.
В большинстве случаев присутствует еще один контакт, Master Clock (MCLK или MCK), он используется для синхронизации приемника и передатчика от одного генератора тактовых импульсов, чтобы снизить коэффициент ошибок передачи данных. Для внешней синхронизации MCLK служат два генератора тактовых импульсов: с частотой 22 579 кГц и 24 576 кГц. Первый, 22 579 кГц, — для частот, кратных 44,1 кГц (88,2, 176,4, 352,8 кГц), а второй, 24 576 кГц, — для частот, кратных 48 кГц (96, 192, 384 кГц). Также могут встречаться генераторы на 45 158,4 кГц и 49 152 кГц — наверняка ты уже заметил, как в мире цифрового звука всё любят умножать на два.
Frame, или кадр I2S
В I2S обязательно используются три контакта: SCK, WS, SD — остальные контакты опциональны.
По каналу SCK передаются синхроимпульсы, под которые синхронизированы кадры.
По каналу WS передается длина «слова», при этом используются и логические состояния. Если на контакте WS логическая единица, значит, передаются данные правого канала, если ноль — данные левого канала.
По SD передаются биты данных — значения амплитуды звукового сигнала при квантовании, те самые 16, 24 или 32 бита. Никаких контрольных сумм и служебных каналов на шине I2S не предусмотрено. Если данные при передаче потеряются, возможности восстановить их не существует.
На дорогих ЦАП часто бывают внешние разъемы для подключения к I2S. Использование таких разъемов и кабелей может плохо отразиться на звуке, вплоть до появления «артефактов» и заиканий, все будет зависеть от качества и длины провода. Все же I2S это внутрисхемный разъем, и длина проводников от передатчика до приемника должна стремиться к нулю.
Рассмотрим, как передается поток данных PCM по шине I2S. Например, при передаче PCM 44,1 кГц с разрядностью 16 бит длина слова на канале SD будет соответствовать этим шестнадцати битам, а длина кадра будет 32 бита (правый канал + левый). Но чаще всего передающие устройства используют длину слова 24 бита.
При воспроизведении PCM 44,1 × 16 старшие биты либо попросту игнорируются, так как заполнены нулями, либо, в случае со старыми мультибитными ЦАП, они могут перейти на следующий кадр. Длина «слова» (WS) может также зависеть от плеера, через который воспроизводится музыка, а также от драйвера устройства воспроизведения.
Альтернативой PCM и I2S может быть запись звукового сигнала в DSD. Этот формат развивался параллельно с PCM, хотя и тут теорема Котельникова оказала некоторое влияние. Для улучшения качества звучания по сравнению с CDDA упор был сделан не на повышение разрядности квантования, как в формате DVD Audio, а на увеличение частоты дискретизации.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is DSD music?
DSD music is computer audio files in Direct Stream Digital format. This format consumes significant hard disk space and is intended for music lovers, primarily. Read details below.
What is DSD music format?
DSD music format is an audiophile format, that solves issues of 16 bit/44.1 kHz CD resolution. This music format is available in DSF, DFF, SACD ISO files. Read details…
Read more: How to improve sound quality…
What is DSD music file?
DSD audio files are files, that capable of contains DSD audio content: DSF, DFF, SACD ISO and DoP FLAC, WAV, etc. Read details here…
Is DSD better than FLAC?
No single answer the question. Actual sound quality depend on recording and playback music system. Read about comparison DSD and FLAC…
Is DSD audio worth it?
In general case, DSD allow to solve some issues of ADC and DAC analog filters on lower sampling rates. Potentially, it gives advantages of sound quality. But each case should be considered separately, because recording quality and audio system implementation does matter. Read details…
What is DFF audio file?
DFF file is one of DSD files. Its audio data content is identical to DSF by the sound quality. Read DFF file details here…
What are DSD files?
DSD files (.dsf, .dff, .iso , DoP FLAC, WAV, others) are files, that contains DSD audio data. Read details…
DSD256 is sample rate 11.3 MHz=44100 Hz * 256;
DSD512 is sample rate 22.6 MHz=44100 Hz * 512. Read more…
Is DSD better than PCM?
Only audio system implementation define sound quality. However, potentially, DSD gives some design advantages to achieve better sound quality. Read more…
Read more:
How to extract ISO >
How to convert DSF >
How to convert DFF >
DSF vs DFF vs SACD ISO (infographic) >
DSF vs DFF (details) >
DSD DAC >
If you want to add new information, change the wrong one, send feedback, contact us, please.
Read other articles about audio issues
What is Hi-Res Audio? | Where are Free Downloads?
How to Open DSF Audio Files
Audio Converter List | Read Comparison
DSD vs FLAC
DSD vs DSF vs DFF Files Audio. What is difference
R2R Ladder DAC vs Sigma-Delta DAC vs DSD DAC
July 07, 2020 updated | since April 20, 2018
How to play DSD?
Free DSD downloads >
Free Hi-Res downloads >
Free DSD converters >
Free DSD players >
DSD64 vs 128 vs 256 >
DSD may be played at a mobile phone, portable players, music servers, SACD-players and other devices.
Some device can support native DSD feed of DSD DACs. Other ones demand pre-conversion to PCM or make conversion «on fly».
Sound quality is a complex matter. Read details about the resolution of audio files and sound quality.
Read details how to open, play DSD on Mac, Windows, iOS, Android, Linux: player list >
Read how to download DSD music and how to get free DSD files here >
DSD audio players (hardware and software) can playback all or some of the 1-bit file formats.
1-bit files may be played back directly on DSD DAC/player or converted to PCM «on fly» to playback to PCM DAC/player. About SACD conversion read more
1-bit playback may be performed via special ASIO-driver under Windows, including DoP (DSD over PCM) digital audio packing format (example).
SACD optical disks may be played back at hardware player. Author knows nothing about available SACD-drives for consumer computers to playback/record SACD optical disks.
A stereo player may downmix multichannel to stereo. As alternative multichannel files may be pre-converted to stereo. It allows saving space on the hard disk of an audio player. Downmix is lossy audio processing. Its quality defined by an implementation.
Read more about the players here > and
Read DSD player software list >
DSD player brief F.A.Q.
-
Can foobar2000 play DSD?
Yes. Read details here
-
Can VLC play DSD files?
As the author know, not. Details
-
Can Jriver play DSD files?
Yes. Look at the player list
-
Can Vox play DSD?
As the author know, Vox convert .dsf and .dff files to PCM on fly without native DSD playback.
- Can Plex play DSD?
-
Can Amarra play DSD?
Yes
-
Can Audirvana play DSD?
Yes
-
Can iPhone play DSD files?
Yes. Look at the player list
-
Can iPod play DSD?
As the author knows, there is conversion to PCM files is necessary.
-
Can Mac play DSD?
Yes
Also read: , ,
DSD editing software
Read main article about DSD editing >
DSD editing is sophisticated issue due modulation noise. Non-linear processing can cause audible intermodulation distortions by ultrasound noise.
Currently no information, that is known for the author, about «native» 1-bit processing (example: gain altering, resampling, etc.) without conversion 1-bit to multibit and back. Except, merging/dividing the audio file.
Read the article about DSD versus DSF versus DFF >
DSD editing

PCM here may be considered as «multibit DSD». Pulse code modulation is not obligatory to mean «24 bit / 352 kHz» or so on. Author recommends use 32- or 64-bit float point bit depth. This PCM contains high frequency modulation noise. But for conversion, this «multibit DSD» to 1-bit need re-modulation with .
Losses of editing with 1-bit/multibit conversion are comparable with resampling.
Recording studios may distribute 1-bit records without editing.
There is DXD format. It is PCM (as rule «24 bit / 352 kHz» or so on) with high sample rate and bit depth and legacy DSD noise. However, the noise can cause audible intermodulation distortions. Before non-linear processing, the high frequency noise cutting is recommended.
Watch and share: Experiment with cutting ultrasound noise
Какие бывают файлы DSD?
Сейчас два самых популярных формата — DFF и DSF. Различаются между собой они примерно как WAV и FLAC. Оба форматы «без потерь», оба обеспечивают максимальное качество, но вот DFF не поддерживает ни компрессию, ни тэги файлов, тогда как DSF поддерживает и то и другое.
Что касается качества, то базовым стандартом считаются файлы DSD64 с частотой дискретизации 2.8 Мгц. Существуют также стандарты DSD128, DSD256 и DSD512, в каждом последующем случае частота дискретизации увеличивается в два раза. Нам же нужно запомнить не эти потоки цифр, а только то, что каждый Цифро Аналоговый Преобразователь (ЦАП) с поддержкой DSD явно указывает, до какой частоты принимает потоки. Естественно, что самые последние микросхемы могут обрабатывать DSD512, но в реальной жизни все проще — подавляющее большинство записей существует в DSD64, очень немногие современные записи были выпущены в DSD128, а DSD256 и DSD512 — пока только в виде тестовых записей.
DSD history
Free DSD downloads >
Free Hi-Res downloads >
Free DSD converters >
Free DSD players >
DSD64 vs 128 vs 256 >
Audio CD optical disk (PCM modulation / PCM format) was one of first digital formats. It was a source with low distortion and noise level comparing analog ones. I think, now many people forgot what is «real analog noise».
From CD (PCM) to SACD (DSD)
After CD, demands to sound quality improvements could be implemented by increasing sample rate or bit depth.
Audio quality (sound quality) is a level of noise and distortions, that cause format/software/equipment. The level may be normalized by psychoacoustic criteria.
However, Sony and Phillips decided to use another kind of modulation — 1-bit sigma-delta modulation. At first glance, using of 1-bit is impossible, because such bit depth (resolution) causes huge noise level. But, if high sample rates are used, noise energy may be pushed out of audible frequency range (to ultrasound). That action is called «».
Practically, 1-bit conception may be easier, than multi-bit, in a DAC implementation (read below).
When DSD music is converted to analog, ultrasound noise is filtered.
Medium, that contains 1-bit DSD audio stream was called SACD (Super Audio CD).
Look at DSD file infographic >
What is Hi-Res audio? How it works? Why does High-Resolution is need?
Free DSD downloads >
Free Hi-Res players >
Free Hi-Res converters >
- High resolution audio (hi-res audio, high-definition audio) is musical formats (digital signals) with resolutions above 16 bit/44.1 or 48 kHz, including 1-bit DSD (Direct Stream Digital).
- Hi-res music is intended to get better listener experience, than standard CD-audio, via higher sound quality.
- It is one of widespread audiophile and music production terms.
Medium comparison (lossy, CD, Hi-Res, vinyl, tape),
click to enlarge to see more details
At the picture we can see approximate artistic visualisation of format difference. It is not real differing. Implementation of the musical systems is matter. But we can see general trends.
«Wow and flutter» is sound altering due fluctuations of speed tape or vinyl record rotation.
«Tape compression» is non-linear distortions about overload, that reduce output level softly, when input level is increased linearly.
Some colourization can cause more «nice»/»interesting look» of analog mediums, than digital sources, that are closer to the original sound source.
When vinyl recording is produced from tape one, their distortions are merged complicated way.
High resolution has not these «analog» issues and may have lesser aliases (shifted copyes of original signal) comparing 44.1 kHz. Read explanation below.
Read also:
- Analog vs Digital
Why does Hi Res audio need?
Hi-res audio was designed to provide higher sound quality and better listener experience, than standard CD-audio. Read below: is the aim achieved or not?
PCM 44.1 kHz / 16 bit vs. High resolution: PCM and DSD
Issues of music a genres
Some kinds of music with a wide range of instrument loudness (like classical, jazz), demands a wider dynamic range of a musical system.
The range may be achieved via increasing of resolution.
High resolution recordings were invented for music with wide loudness range
Digital recording issues
We havn’t full control of recorded level. As example, in classical music recordings. Digital recording demands some tricks to avoid analog and analog-to-digital conversion overload distortions, that can not be fixed after record.
Overload is output level is stop changing when input one continues to grow.
ADC overload
However, reducing of analog signal level at analog-to-digital converter (ADC) input can cause worse signal-to-noise ratio. Especially, for low-level fragments of a musical piece.
So, ADC should have wider dynamic range, to reduce risk of damaging of recorded signal.
In general, noise level of digital representation of an analog signal (quantization noise), should be lower, than ADC’s own electrical noise (relative overload level).
Example:
ADC’s maximal level is 0 dB and noise floor is -120 dB.
We record a symphony orchestra in 2 microphones.
To avoid overload, we reduce input analog level of ADC. It give some loudness reserve. But it degrade signal-to-noise ratio of quiet musical fragments. More reserve is more the degradation.
If we use lower bit-depth resolution, it can cause quantization noise, that is higher than noise floor of the DAC. And the signal-to-noise ratio get more degradarion.
Digital Signal Processing
However, resolution of further digital signal processing (DSP), may be increased, to «transparent» (for DSP designers) work with sound.
Read more and details in «Why depth above 16 bit is need» part below.
There are many questions about the necessity of hi-resolution musical recordings.
One people thinks, that «excessive» resolution waste disk space only.
Other people think, that such records are needed to produce ultrasound.
But, by author opinion, existing of high-res may be useful and have other reasons. Read «Myths» part below.
High-resolution audio file formats
(sample rates)
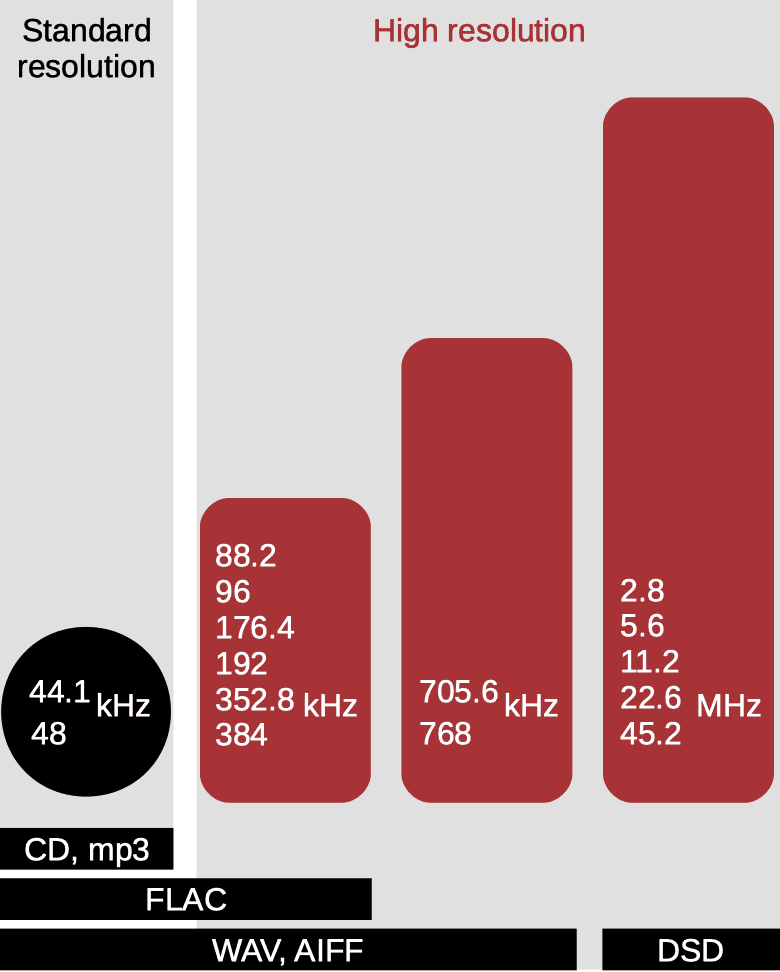
High-resolution music file formats
(bit-depths)
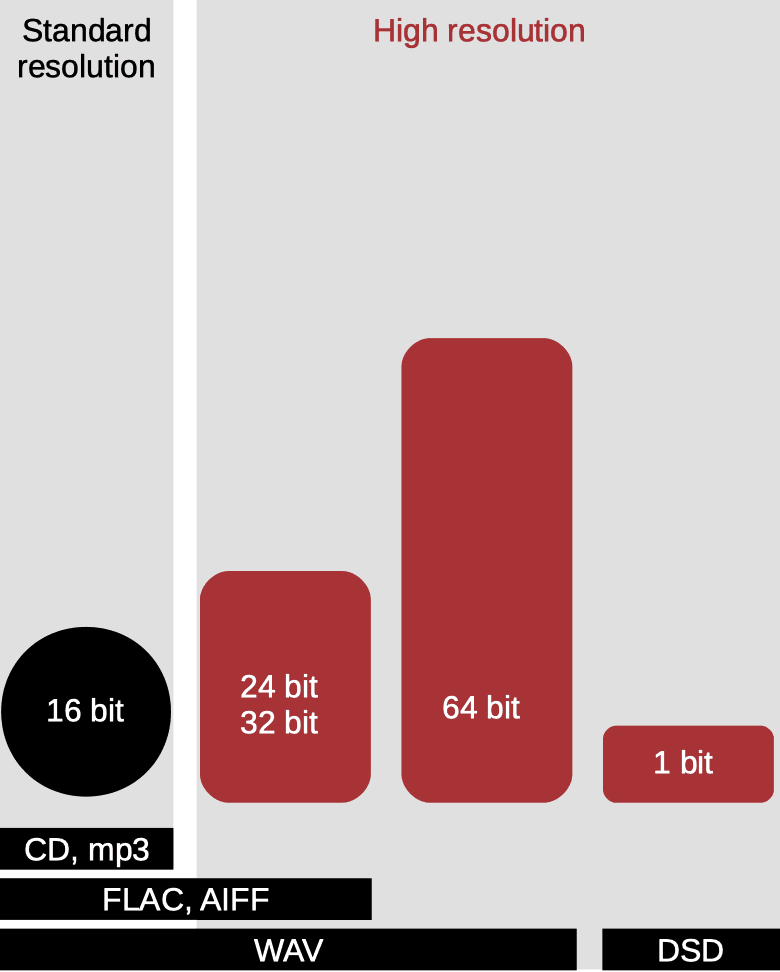
Opinion, that high res gives advantages always, is not correct for all cases.
Sometimes people, who play records with high sample rates, stumble with unexpected noise or other unwanted sounds.
In «Myths» part you can watch the video with example.
Watch and share: What is DSD? Video explanation
Hi-res playback
Hi resolution may be played back at:
- computers,
- portable audio players,
- mobile phones ,
- tablet computers,
- music servers,
- SACD and BlueRay players,
- etc.
Separate device may be used to connect to a mobile phone, portable player, computer and etc.
There are high res musical players Mac, Windows , iPhone, Android.
High-res audio converters
Audiophile and professional audio conversion software should provide a wide range of sample rates and bit-depth, including 32-/64-bit.
DSD music downloads
If you are interested where to find DSD music paid and free download resources, look at the table.
| Site | Description | DSD music free download links |
|---|---|---|
| Norwegian audiophile label. At the site link to the store, where DSD 2.8, 5.6 and 11.2 MHz and other file formats are placed | ||
| Store of audio downloads | ||
| Audiophile Inventory | Free test signals in DSF format | Free downloads |
| Audiophile recording label. At the site link to store, where DSD 64, DSD 128, DSD 256 (11.2 MHz) and other formats are placed | ||
| Live Bruce Springsteen site | ||
| Recording label. In the store DSD64, DSD128, DSD256 and other formats are placed | ||
| DSD 64, 128 | ||
| Cybele Records | Recording label, store | |
| Music reseller. D64, D128, D256 and other formats are placed | ||
| Blog | ||
| DSD files | ||
| DSD music file store | ||
| DSD samples | ||
| Online musical store | ||
| The online store of high definition music | ||
| High Definition Tape Transfers | Recording store. DSD64/128/256 and other formats are available | |
| High quality music store | ||
| DSD64, DSD256 | ||
| The online store of hi-res music. Provide dsd files in D64, D128, D256. SACDs are available there too | ||
| DSD64 | ||
| Online music recording store | ||
| Music store: 64fs, 128fs, 256fs DSD and other, stereo and multichannel | ||
| DSD64 | ||
| Audio recordings store | ||
| Oppo Digital | DSD download free music samples | Free downloads |
| DSD music online store | ||
| Streaming service now. Free downloads are not available currently. | ||
| Online store. There are DSF files (2.8 and 5.6 MHz) are placed. | ||
| D64/128/256 (2.0 and 5.1) and other formats | ||
| High-resolution audio including DSD downloads by SONY | ||
| Wechseldominante | Site of Japanese self-publishing music group |
DSD audio file conversion
DFF/DSF to FLAC/WAV >
FLAC/WAV to DSF/DFF >
SACD ISO to FLAC >
SACD ISO to DSF >
DFF/DSF to DSF/DFF >
Split CUE+DSF/DFF >
PCM vs DSD vs DXD vs Analog sound quality
All these formats give musical system designers the same abilities. Final result depends on how music system is done.
PCM has no technological noise «hump» at high frequencies. Direct Stream Digital and DXD have.
So there is no necessity to suppress the noise excess at PCM high frequencies.
However, we don’t hear ultrasound (see details below in «Myths»). And the noise is not audible.
Nevertheless, musical system hardware and, sometimes, software have non-linear distortions.
The distortions can cause the generation of audible products (noise, as rule) by inaudible noise. It’s called as intermodulation distortions. See more
Read about DSD vs PCM >
Watch and share: DSD vs FLAC